How to perform hand hygiene?
Clean your hands by rubbing them with alcohol-based hand sanitizers; as alcohol is the preferred method of routinely disinfecting hands if they are not visibly dirty. This method is quick and more effective and better than washing with soap and water.
Wash your hands with soap and water whenever they are visibly dirty, before eating, and after using the restroom.
How to handrub?
How to handwash?
When to handwash?
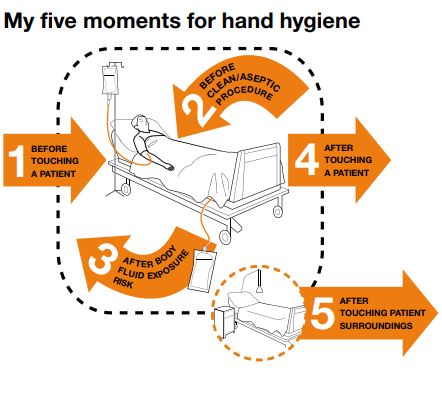
- Before touching a patient:
- Why? To prevent germ transmission from the health-care area to the patient and ultimately to protect the patient against colonization and, in some cases, against exogenous infection by harmful germs carried on health-care workers’ hands.
- when? Before touching a patient when approaching him/her.
- Before clean/aseptic procedure:
- Why? To prevent germ transmission to the patient and from one body site to another in the same patient through inoculation
- when? Immediately before accessing a critical site with infectious risk for the patient, such as any procedure involving any direct and indirect contact with mucous membranes, non-intact skin or an invasive medical device.
- After body fluid exposure risk:
- Why? To protect the health-care worker from colonization or infection with the patient’s germs and to protect the health-care environment from germ contamination and potential subsequent spread
- When? As soon as the task involving exposure risk to body fluids has ended (and after glove removal)
- After touching a patient:
- Why? to protect the health-care worker from colonization and potential infection by patient germs and to protect the environment in the healthcare area from germ contamination and potential spread.
- When? when leaving the patient’s side, after having touched the patient.
- After touching patient surroundings:
- Why? To protect the health-care worker against colonization by patient germs that may be present on surfaces/objects in patient surroundings and to protect the health-care environment against germ contamination and potential spread.
- when? After touching any object or furniture when leaving the patient surroundings, without having touched the patient.